SAP Business Data Cloud (BDC) is a next-generation SaaS solution, officially announced in early 2025, representing SAP’s renewed vision for data management. Designed as a unified platform, BDC brings together in one environment the capabilities of SAP Datasphere, SAP Analytics Cloud, SAP Business Warehouse, as well as partner technologies like Databricks and “Intelligent Applications.” It enables organizations to centralize, govern, and leverage their data — whether from SAP or non-SAP systems — without duplication or loss of business context.
More than just a data warehouse, BDC offers an integrated and intelligent approach to orchestrating the entire data lifecycle by facilitating large-scale access, contextualization, and value extraction.
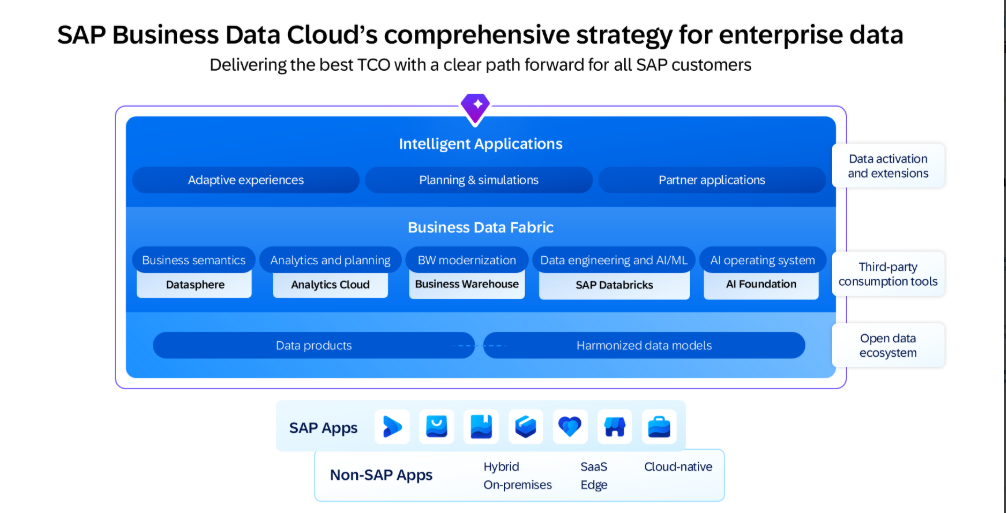
In this article, we’ll explore the key innovations of SAP BDC and their concrete impact on organizations.
1. An Intelligent Data Fabric Architecture
The first major innovation is based on the principle of a data fabric: data is no longer moved unnecessarily.
The concept of a Data Fabric refers to a unified architecture that allows access to, connection with, management, and governance of data wherever it resides — without the need to systematically duplicate or move it.
In the context of SAP Business Data Cloud, an intelligent Data Fabric means that:
-
Data can remain in its source system (SAP or non-SAP)
-
Users can query, combine, and contextualize this data as if it were in a single environment
-
Security, governance, and quality rules are centralized and applied universally
-
Data silos, multiple copies, and manual processing are avoided
In other words, the Data Fabric acts as a layer of intelligence and connection between all of a company’s data sources, with a “query where it lives” approach, providing a seamless, governed, and scalable experience.
2. Native Integration with Cloud Partner Ecosystems
SAP BDC is fully open to strategic partners such as:
-
Databricks: for advanced AI, machine learning, and data engineering
-
Google BigQuery: for large-scale cloud data analytics
-
Snowflake: for fast and scalable analytical processing
-
Collibra: for data governance, cataloging, and compliance
This interoperability enables native connections between these platforms and SAP Datasphere without heavy exports or complex developments. This means that companies can:
-
Maintain their existing architecture while integrating SAP
-
Capitalize on non-SAP investments without technological disruption
-
Promote smooth data flow between business and IT stakeholders
3. Intelligent Applications and Ready-to-Use Data Products
SAP BDC introduces ready-to-use Intelligent Applications that allow users to directly consume advanced analytics within their business processes. These applications can be customized or enriched with new data models, ML logic, and integrated with SAP Analytics Cloud.
At the same time, SAP data products deliver curated, governed, and contextualized datasets for domains like finance, sales, or HR, making them reusable across the organization.
For example, a Finance data product might combine accounts payable, billing, and cash flow data into a standardized, ready-to-use model for financial planning. This product can then be consumed in SAP Analytics Cloud reports or embedded into intelligent processes.
4. A Reimagined Semantic Layer for Business Users
Traditionally, enterprise data is stored in complex technical structures, often unreadable for business users. SAP BDC introduces a new semantic layer that translates these structures into understandable, directly usable business concepts.
In practical terms, this means:
-
Data is no longer exposed as raw technical tables but enriched with business descriptions, hierarchies, units of measure, and harmonized data types
-
Models are accessible via familiar tools like SAP Analytics Cloud, Excel, or third-party BI tools
-
Non-technical users can build their own analyses and dashboards without IT support, based on governed and secure business views
This semantic layer acts as a bridge between raw data and business needs, empowering users, accelerating decision-making, and reducing interpretation errors.
5. Advanced Security, Traceability, and Governance
SAP BDC strengthens data governance by offering:
-
Granular, domain-specific access rules
-
Dynamic masking of sensitive data to ensure confidentiality
-
Rigorous tracking of access and modifications, ensuring full compliance with regulations such as GDPR and ISO certifications
What Does This Mean for Businesses?
For organizations, SAP BDC enables:
-
Simplified reporting chains
-
Reduced data silos
-
Enhanced self-service analytics
-
Improved data quality and reliability
In short, it’s a key step toward a modern, governed, and value-driven data strategy.
Conclusion
SAP Business Data Cloud isn’t just evolving — it’s redefining how companies harness their data. With a unified, connected, and intelligent approach, BDC becomes a central enabler for accelerating digital transformation by putting data at the heart of decision-making.


